

As depicted above, clinicians(MDs, DOs, NPs, PAs) should collaborate to improve patient outcomes. Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine antagonist, is useful in reversing the sedation and respiratory depression that often occur when benzodiazepines are. In addition, medical toxicologist consultation is often required for multiple-drug ingestions. Critical care physician consultation is required in severe poisoning with respiratory depression. Hospital pharmacists should ensure proper dosing of flumazenil. Emergency department physicians should rapidly stabilize the patient. Normally flumazenil overdose is handled by emergency department physicians. Overall, the use of flumazenil to manage benzodiazepine overdose is diminishing as the drug may cause more harm than good. A few patients may develop rhabdomyolysis and aspiration pneumonia. 3 It binds to the extracellular surface of GABA A receptors and competitively displaces benzodiazepine molecules, preventing further benzodiazepine binding. In most isolated cases of benzodiazepine overdose, supportive management may prove useful. Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine analogue with minimal intrinsic activity. The problem arises when the individual has co-ingested alcohol or other illicit drugs. In general, patients who overdose on benzodiazepines alone rarely have significant mortality. The nurse and the pharmacist should educate the patient on the use of benzodiazepines, their potential to cause addiction, and physical dependence. The ideal circumstance for flumazenil is when a naive benzodiazepine individual has overdosed. Additionally, all healthcare workers need to know that this drug should not be used in patients with a history of seizures, head injury, or those who have ingested a tricyclic antidepressant. Evidence in the paper suggests that the sleep-inducing substance in patients’ cerebrospinal fluid is not a benzodiazepine drug, even though flumazenil counteracts it. Usually to reverse procedural sedation, accidental paediatric ingestion with compromise, and rarely to help make a diagnosis of benzodiazepine overdose or if a patient’s airway. Flumazenil is usually used in cases of overdose of benzodiazepines, a widely used class of anesthetics and sedatives such as diazepam (Valium) and zolpidem (Ambien).
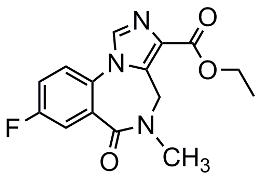
The drug may precipitate seizures and withdrawal in patients who have been using benzodiazepines for a medical disorder. Flumazenil is a competitive benzodiazepine antagonist with a limited role in the management of benzodiazepine poisoning. Not everyone with benzodiazepine overdose will respond to it. Flumazenil is a competitive benzodiazepine antagonist with a limited role in the management of benzodiazepine poisoning. The problem with flumazenil is that its effects are not consistent or predictable. Despite the initial hype about the drug, many experts believe that its risks may outweigh its benefits. This competitive antagonist of benzodiazepines can rapidly reverse benzodiazepine overdose. Today, with the epidemic of drug overdoses, nurses, pharmacists, and physicians need to be aware of flumazenil.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
